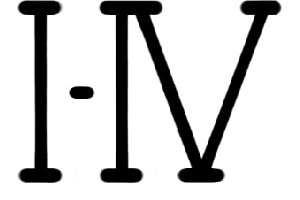PLOT
Siegfried is the third of the four operas that constitute Der Ring des Nibelungen (The Ring of the Nibelung). It is primarily inspired by the story of the legendary hero Sigurd in Norse mythology.
It is the story of a hero, Siegfried, and how he grows into manhood to discover fear and love. Raised by the Nibelung Mime, Siegfried is young, innocent and cocky. With the help of a mysterious Wanderer (who is really Wotan in disguise), Siegfried finds the pieces of his father's sword, Notung, reforges them and uses the instrument to kill the dragon Fafner who guards the hoard of Nibelung gold that formerly belonged to the Rhinemaidens.
As a result of his killing of Fafner, Siegfried comes into possession of Alberich's cursed ring. But, Siegfried faces his ultimate challenge when he follows a birdsong to find the sleeping Brünnhilde whom fate has destined Siegfried to awaken and fall in love with. At the end of the opera, Siegfried gives the Ring to Brünnhilde to prove and symbolize his oath of love and fidelity to her.
ACT BY ACT
Opera in 3 acts
Sung in German
About 4 hours + intervals
Act 1
Scene 1
A cave in rocks in the forest. As the curtain rises, Alberich's brother, the dwarf Mime, is forging a sword. Mime is plotting to obtain the ring of power originally created by his brother Alberich. He has raised the human boy Siegfried as a foster child, to kill Fafner, who obtained the ring and other treasures in the opera Das Rheingold and has since transformed himself from a giant to a dragon. Mime needs a sword for Siegfried to use, but the youth has contemptuously broken every sword Mime has made. Siegfried returns from his wanderings in the forest with a wild bear in tow, and immediately breaks the new sword. After a whining speech by Mime about ingratitude, and how Mime has brought him up from a mewling infant ("Als zullendes Kind"), Siegfried senses why he keeps coming back to Mime although he despises him: he wants to know his parentage. Mime is forced to explain that he encountered Siegfried's mother, Sieglinde, when she was in labor; she died giving birth to Siegfried. He shows Siegfried the broken pieces of the sword Nothung, which she had left in his custody. Siegfried orders him to reforge the sword; however, Mime is unable to accomplish this. Siegfried departs, leaving Mime in despair.
Scene 2
An old man (Wotan in disguise) arrives at the door and introduces himself as the Wanderer. In return for the hospitality due a guest, he wagers his head on answering any three questions Mime may ask. The dwarf asks the Wanderer to name the races that live beneath the ground, on the earth, and in the skies. These are the Nibelung, the Giants, and the Gods, as the Wanderer answers correctly. The Wanderer then induces Mime to wager his own head on three further riddles: the race most beloved of Wotan, but most harshly treated; the name of the sword that can destroy Fafner; and the person who can repair the sword. Mime answers the first two questions: the Wälsungs (Siegmund and Sieglinde whose tale is told in the opera Die Walküre) and the sword Nothung. Mime has no problem with the first two questions, but cannot answer the last one. Wotan spares Mime, telling him that only "he who does not know fear" can reforge Nothung, and leaves Mime's head forfeit to that person.
Scene 3
Mime despairs as he imagines the ferocity of the dragon Fafner, while "the orchestra paints a dazzling picture of flickering lights and roaring flames". Siegfried returns and is annoyed by Mime's lack of progress. Mime realizes that Siegfried is "the one who does not know fear" and that unless he can instill fear in him, Siegfried will kill him as the Wanderer foretold. He tells Siegfried that fear is an essential craft; Siegfried is eager to learn it, and Mime promises to teach him by taking him to Fafner. Since Mime was unable to forge Nothung, Siegfried decides to do it himself. He succeeds by shredding the metal, melting it, and casting it anew. In the meantime, Mime brews a poisoned drink to offer Siegfried after the youth has defeated the dragon. After he finishes forging the sword, Siegfried demonstrates its strength by chopping the anvil in half with it.
Act 2
Scene 1
Deep in the forest. The Wanderer arrives at the entrance to Fafner's cave, where Alberich is keeping vigil. The two enemies recognize each other. Alberich boasts of his plans to regain the ring and rule the world. Wotan states that he does not intend to interfere, only to observe. He even offers to awaken the dragon so that Alberich can bargain with him. Alberich warns the dragon that a hero is coming to kill him, and offers to prevent the fight in exchange for the ring. Fafner dismisses the threat, declines Alberich's offer, and returns to sleep. Wotan leaves and Alberich withdraws, muttering threats.
Scene 2
At daybreak, Siegfried and Mime arrive. After assuring Siegfried that the dragon will teach him what fear is, Mime withdraws. As Siegfried waits for the dragon to appear, he hears a woodbird singing. He attempts to mimic the bird's song using a reed pipe, but is unsuccessful. He then plays a tune on his horn, which brings Fafner out of his cave. After a short exchange, they fight; Siegfried stabs Fafner in the heart with Nothung. In his last moments, Fafner learns Siegfried's name, and tells him to beware of treachery. When Siegfried withdraws his sword from Fafner's body, his hands are burned by the dragon's blood and he puts his finger in his mouth. On tasting the blood, he finds that he can understand the woodbird's song. Following its instructions, he takes the ring and the magic helmet Tarnhelm from Fafner's hoard.
Scene 3
Outside the cave, Alberich and Mime quarrel over the treasure. Alberich hides as Siegfried comes out of the cave. Siegfried complains to Mime that he has still not learned the meaning of fear. Mime offers him the poisoned drink; however, the magic power of the dragon's blood allows Siegfried to read Mime's treacherous thoughts, and he stabs him to death. He throws Mime's body into the treasure cave and places Fafner's body in the cave entrance to block it. The woodbird now sings of a woman sleeping on a rock surrounded by magic fire. Siegfried, wondering if he can learn fear from this woman, follows the bird towards the rock.
Act 3
Scene 1
At the foot of Brünnhilde's rock. The Wanderer summons Erda, the earth goddess. Erda, appearing confused, is unable to offer any advice. Wotan informs her that he no longer fears the end of the gods; indeed, it is his desire. His heritage will be left to Siegfried the Wälsung, and Brünnhilde (Erda's and Wotan's child), who will "work the deed that redeems the World." Dismissed, Erda sinks back into the earth.
Scene 2
Siegfried arrives, and the Wanderer questions the youth. Siegfried, who does not recognize his grandfather, answers insolently and starts down the path toward Brünnhilde's rock. The Wanderer blocks his path, but Siegfried mocks him, laughing at his floppy hat and his missing eye, and breaks his spear (the symbol of Wotan's authority) with a blow from Nothung. Wotan calmly gathers up the pieces and vanishes.
Scene 3
Siegfried passes through the ring of fire, emerging on Brünnhilde's rock. At first, he thinks the sleeping armored figure is a man. However, when he removes the armor, he finds a woman beneath. At the sight of the first woman he has ever seen, Siegfried at last experiences fear. In desperation, he kisses Brünnhilde, waking her from her magic sleep. Hesitant at first, Brünnhilde is won over by Siegfried's love, and renounces the world of the gods. Together, they hail "light-bringing love, and laughing death."
ROLES
Siegfried - Tenor (Helden)
The son of Siegmund and Sieglinde
Mime – Tenor (charakter)
A Nibelung, brother of Alberich
Wotan (Der Wanderer) – Bass-baritone (dramatic)
The god Wotan disguised as a mortal, grandfather of Siegfried
Alberich – Baritone (dramatic/charakter)
A Nibelung, brother of Mime
Fafner – Bass (basso profondo)
A giant who has been transformed into a dragon
Waldvogel – Soprano (lyric coloratura)
A forest bird
Erda – Contralto
The goddess of the earth
Brünnhilde – Soprano (dramatic)
A former Valkyrie who is now mortal
COMPOSER
Richard Wagner
1813-1883
Place of birth: Leipzig, Germany
Place of death: Venice, Italy

BIOGRAPHY
Richard Wagner was a 19th century German composer, theatre director, conductor and librettist. His writing period spans over more than 50 years. He is most known for his operas, what he called, "music dramas". Particularly in his later operas he made use of "Leitmotifs" (leading motifs), musical phrases connected to a role character, a place or an idea. He also describes the music dramas as "Gesamtkunstwerk" (total work of art). This idea revolutionised opera. By combining poetic, visual, musical and dramatic arts the story could unfold with the music supporting the drama.
Wagner's hostile writings expressing antisemitic views have been widely commented. Hitler was an admirer of his music and there are continuous debates about the extent to which Wagner's views might have influenced Nazi thinking.
Wagner married Wilhelmine "Minna" Planer in 1836. Their tumultuous marriage would last until Minna's death in 1866, although their relationship ended much earlier. In 1852 Wagner became infatuated with the poet-writer Mathilde Wesendonck. He would set five of her verses to music, the Wesendonck Lieder. In 1863 Wagner met Cosima von Bülow, the wife of Hans von Bülow and daughter of Franz Liszt. They had an affair that would lead to a marriage that would last until Wagner's death. They married in 1870 and had three children.
Wagner's legacy to the world of opera is of considerable scope, although controversial.
COMPOSER'S QUOTE
"Imagination creates reality."
FUN FACTS
Wagner built his own opera house, the Bayreuth Festspielhaus, specifically to house his own works during the annual festival, the Bayreuth Festival. Today audiences travel from all over the world to visit the summer festival. The orchestra pit is designed so that it doesn't draw any attention from the stage, with the orchestra members hidden under the stage, invisible to the audience.
Most prominent operas
Der fliegende Holländer 1843
Tannhäuser 1845
Lohengrin 1850
Tristan und Isolde 1865
Die Meistersinger von Nürnberg 1868
Das Rheingold 1869
Die Walküre 1870
Siegfried 1876
Götterdämmerung 1876
Parsifal 1882
LIBRETTO
Richard Wagner
1813-1883
Der Ring des Nibelungen, also called The Ring cycle, is a cycle of four epic music dramas, Das Rheingold, Die Walküre, Siegfried and Götterdämmerung. The works are based loosely on characters from the Norse sagas and the Nibelungenlied.
Siegfried is the third of the four operas in Wagner's ring. The librettos were written in reverse order. Die Walküre was the second text to be written.
Wagner wrote the libretto for all of his operas and referred to the texts as "poems".
SCORE
DOWNLOAD THE SCORE
INSTRUMENTATION
4d1, 4d1, 4d1, 3 - 8d4, 3+1, 4d1, 1
timp, perc, 6 harps, large string section
stage: horn, English horn
CONTEXT
Siegfried premiered at the Bayreuth Festspielhaus in 1876, as part of the first complete performance of The Ring cycle.
VIDEOS
FULL LENGTH OPERA
Act 1
Duet - Notung! Notung! Neidliches Swchwert (Siegfried, Mime)
Act 2
Aria - Haha! Da Hätte Mein Lied (Siegfried)
Act 3
Aria – Evig war ich (Brünnhilde)